Realistic behaviour in 3D
How do flexible hoses behave under the influence of their mechanical dimensions and properties?
Read more
3D-real-time mechanical design, optimization and digital validation of hoses and tubes

How do flexible hoses behave under the influence of their mechanical dimensions and properties?
Read more

Hose systems must have both superior strength, thermal and dimensional stability.
Read more

The development of brake systems triggers the need for reliable brake hoses.
Read more

Different types of tubes, hoses or grommets are used, for example, to transmit hydraulic pressure, negative pressure or coolant. These include air intake hoses, coolant hoses, fuel hose, brake hose or the engine control unit (vacuum and overpressure hoses).
Worn or torn hoses can leak, which can have a negative effect on vehicle functionality.
These hoses are affected by a natural ageing process and therefore have a limited lifecycle. The selection of components must be adapted to the respective application. The hose resistance, temperature range and bending radius play a decisive role in the application duration of the hose system.
These products are regarded as safety-critical parts and therefore play a decisive role in the development of vehicles and components.
In order to take all these aspects into account in the 3D mechanical design of various hoses and tubes in modern vehicles, IPS Cable Simulation provides the real-time capability for this task and helps engineers to obtain reliable results without long iteration cycles or extensive prototyping.

 Show video
Show video
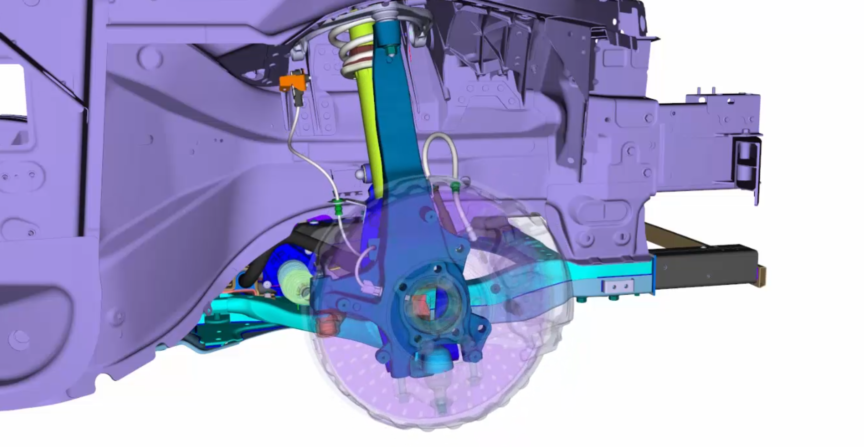
The dynamic behaviour on cables and hoses can play a decisive role in the suspension (sensor cable or brake hose). ... See more
Rapid changes in motion or high frequencies based on excitation during compression and rebound in the suspension can result in dynamic effects that can be simulated with the dynamic module after the quasi-static design in IPS.
As a result, the user receives a virtual validation of dynamic influences on flexible components to examine the layout, design space and durability in order to reduce hardware prototypes.
See less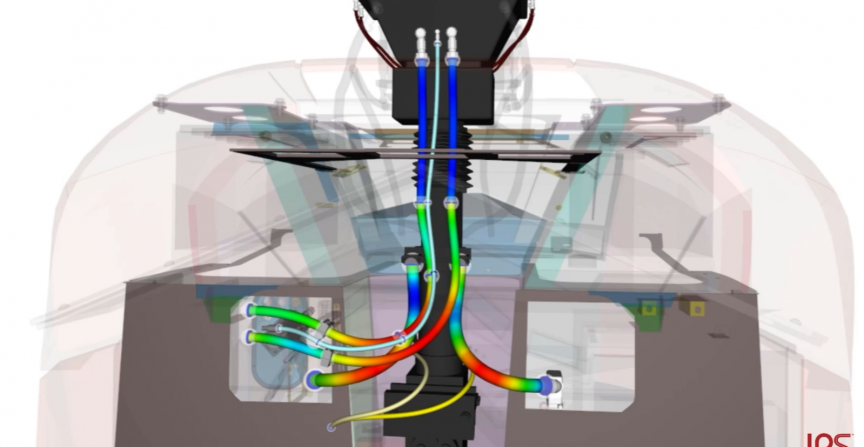 Show video
Show video
Are you interested in the challenges of cables and hoses at a railway front coupling? Find out how to correctly do a 3D mechanical design of these flexible parts. ... See more
At the front coupling of a railway there are various flexible parts that need to be considered and designed realistically, such as cables for power and signal transmission, grounding cables or compressed air hoses for air transmission between trains to ensure the function of the coupler.These increased requirements lead to the need for a virtual validation method without hardware testing and empirical values. With IPS Cable Simulation there is a software solution to meet the following tasks in a fully digital way at the early stages of the product development process.
– 3D mechanical design of hoses and cables in real-time
– Correct length and design right from the start
– Flexible components under the influence of motions
– Fullfillment of assembly requirements
– Consideration of cable stiffness
– First virtual realistic behavior of cables and hoses
 Show video
Show video
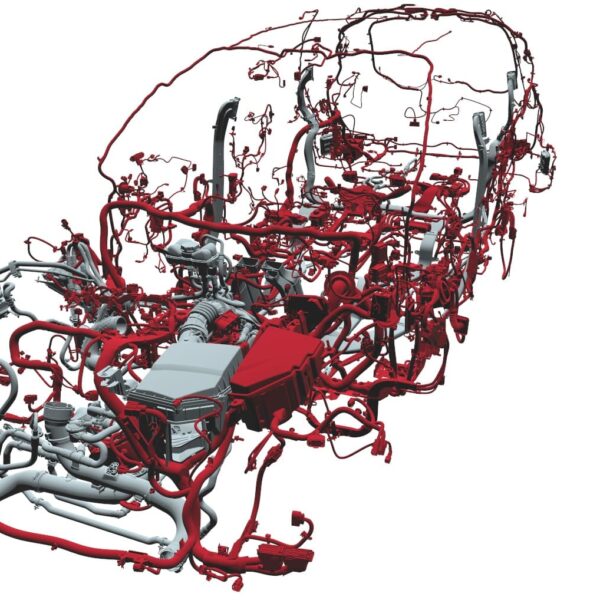
This design project was concerned with the ideal length of hoses in the engine compartment, which is necessary to analyze the stress during engine movement. ... See more
For this purpose, the CAD model of the vehicle was loaded into IPS Cable Simulation, the hoses were automatically flexibilized using the specified connection points and the kinematic movement mapped. The hose lengths were varied and the respective stress was displayed by the software in real time. Thus the optimum length could be successfully determined. In addition, material stress and installation space requirements were reduced considerably, since IPS Cable Simulation can be used to determine the optimum routing with the fastening points for clips and hose guides.
See less


Take full control of your cables and hoses with IPS Cable Simulation. Real time simulation of flexible materials.
Explore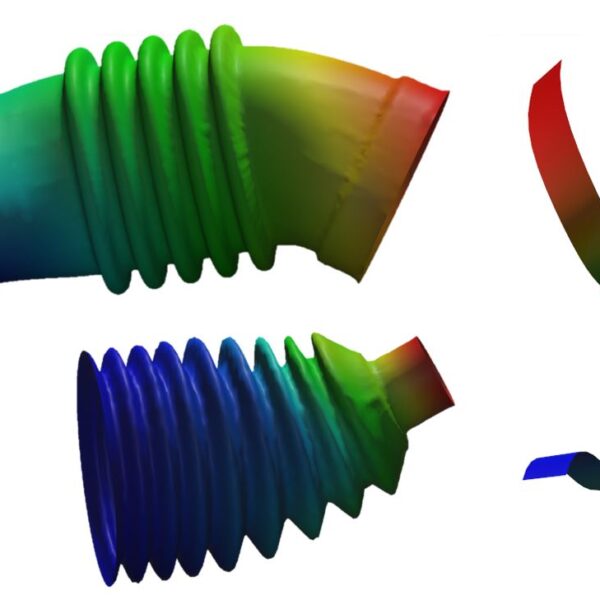
Simulate flexible, moving bellows and grommets with fine structures using a fast FEM-based approach. Flat Cables is a tool for fast and realistic simulations of flat cables. Flexible objects are defined by their physical dimensions in 2D, along with a thickness parameter for the third dimension, and material parameters.
Explore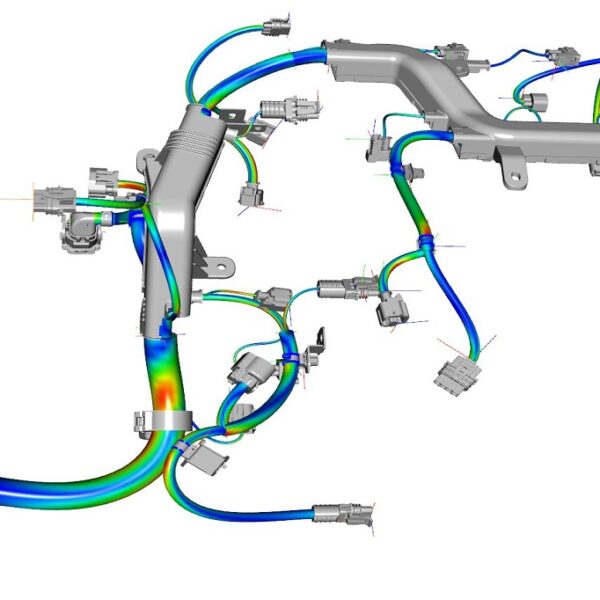
In numerous technical products, cables and hoses are exposed to dynamic excitations. These excitations can have a direct influence on the component behavior and its durability. The Durability and Dynamics module offers the possibility of reducing the number of physical prototypes in the long term and thus optimizing your development process.
ExploreHave a look at the virtual showroom of fleXstructures where we present all of our virtual events & webinars.
In addition, you can get information on our solutions, check out relevant industrial use cases on wiring harness and hose design, validation and human centered assembly in various domains such as automotive, construction machinery, railway or motorcycle on this platform.
You will also find explaining videos which show how tasks can be solved in IPS and guide you through a simulation step by step.

